Image Segmentation
Function Description
Image segmentation is a technique that precisely separates different objects or regions in an image. Unlike traditional image processing, image segmentation can identify which object each pixel in an image belongs to, achieving precise object separation and returning the contour or mask information of each object.
Supported Model
How to Call the Interface
Prerequisites
- Obtain an API Token (create from MoLiArk Console)
- An image to process (local file or network image URL)
Python Call Example
import requests
API_URL = "https://ai.gitee.com/v1/images/segmentation"
API_TOKEN = "<your_api_token>" # Replace with your actual token
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {API_TOKEN}"
}
def cut_image(image_path, prompt=""):
data = {
"model": "sam3",
"prompt": prompt
}
if image_path.startswith(("http://", "https://")):
# Network image: pass URL directly
data["image"] = image_path
response = requests.post(API_URL, headers=headers, data=data)
else:
# Local image: upload via file
with open(image_path, "rb") as image_file:
files = {
"image": (image_path, image_file, "image/jpeg")
}
response = requests.post(API_URL, headers=headers, files=files, data=data)
return response.json()
# Example 1: Segment people in a local image
result = cut_image("path/to/your/photo.jpg", prompt="person")
print(f"Found {result['num_segments']} people")
# Example 2: Segment all objects in a network image (without prompt)
result2 = cut_image("https://example.com/image.jpg")
print(f"Recognized {result2['num_segments']} objects")
Interface Parameter Description
| Parameter Name | Type | Required | Description | Example Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| model | string | Yes | Model name, fixed as sam3 | "sam3" |
| image | file/string | Yes | Image file / network image URL | Local file / "https://..." |
| prompt | string | No | Prompt word, specify objects to segment | "person", "car", "dog,cat" |
Processing Return Results
Result Data Structure
The interface returns data in JSON format, containing the following fields:
{
"num_segments": 3,
"segments": [
{
"id": 1,
"label": "person",
"confidence": 0.95,
"bbox": [120, 80, 320, 450],
"mask": {
"encoding": "rle",
"size": [512, 512],
"counts": "H4sIAAAAAAAA..."
}
},
{
"id": 2,
"label": "dog",
"confidence": 0.87,
"bbox": [350, 300, 480, 420],
"mask": {...}
}
]
}
Mask Decoding Method Explanation (Frontend/Client)
The mask field returned by the interface is COCO RLE counts, which needs to be decoded with image height and width to obtain an H × W 2D 0/1 mask matrix.
RLE Decoding Example (JavaScript)
/**
* Decode COCO RLE format mask
* @param rleString - RLE encoded string
* @param height - Image height
* @param width - Image width
* @returns 2D array [height][width], 1 indicates foreground, 0 indicates background
*/
export function rleDecode(
rleString: string,
height: number,
width: number,
): number[][] {
rleString = atob(rleString);
// Decode RLE counts
const counts: number[] = [];
let p = 0;
while (p < rleString.length) {
let x = 0;
let k = 0;
let more = true;
while (more) {
const c = rleString.charCodeAt(p) - 48;
x |= (c & 0x1f) << (5 * k);
more = (c & 0x20) !== 0;
p++;
k++;
if (!more && (c & 0x10) !== 0) {
x |= -1 << (5 * k);
}
}
if (counts.length > 2) {
x += counts[counts.length - 2];
}
counts.push(x);
}
// Create flat array from RLE counts (column-first order)
const total = height * width;
const mask = new Uint8Array(total);
let pos = 0;
let val = 0;
for (const count of counts) {
for (let i = 0; i < count && pos < total; i++) {
mask[pos] = val;
pos++;
}
val = 1 - val; // Switch between 0 and 1
}
// Convert flat array to 2D array (column-first to row-first)
const result: number[][] = Array.from({ length: height }, () =>
new Array(width).fill(0),
);
// COCO RLE uses column-first (Fortran) order storage
let idx = 0;
for (let x = 0; x < width; x++) {
for (let y = 0; y < height; y++) {
if (idx < total) {
result[y][x] = mask[idx];
idx++;
}
}
}
return result;
}
You can visit the MoArk Example Code Repository to reference more example code.
Online Experience
You can also directly experience the image segmentation function online.
Usage Method
Upload reference image → Input prompt → Click run
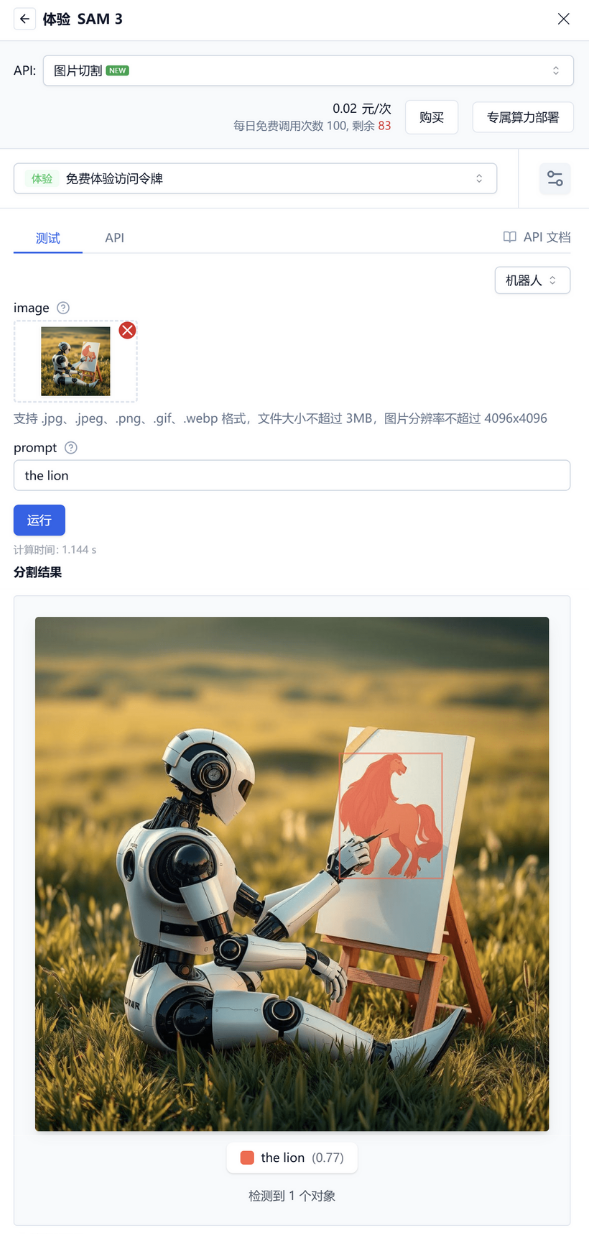
Example Effects
| Reference Image | prompt | Result |
|---|---|---|
 | kids |  |
 | apple |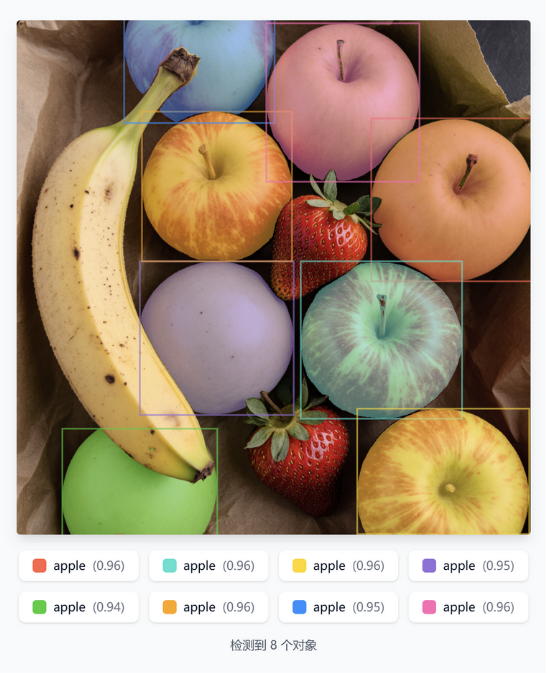  |
Usage Scenarios
Through the image segmentation interface, you can quickly add advanced visual analysis capabilities to your applications without training models or building complex infrastructure, enjoying pixel-level precision image understanding services:
Basic Usage Scenarios
- Intelligent matting: Automatically separate subjects like people, products, etc., and remove backgrounds
- Object counting: Count specific objects in images
- Image annotation: Prepare annotation data for training AI models
Practical Applications
# Example 1: E-commerce product matting
product_result = cut_image("product_photo.jpg", prompt="shoes, handbag")
# Get precise contours of each product for creating transparent background product images
# Example 2: Surveillance video analysis
security_result = cut_image("camera_feed.jpg", prompt="person, vehicle")
# Identify people and vehicles in the scene for security monitoring