Fine-Tuning Models with LoRA
Feature Description
LoRA refers to Low-Rank Adaptation, a method for fine-tuning pre-trained models. LoRA can adapt to new tasks by introducing low-rank matrices without altering the weights of the pre-trained model. In text-to-image and image editing tasks, LoRA can be used to fine-tune pre-trained image models, enabling them to perform better on specific tasks.
Models Supporting LoRA
- Flux.1-dev
- Flux.1-schnell
- Flux.1-Kontext-dev
- InstantCharacter
- OmniConsistency
- stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0
Experience the API Effect
Function Description
The Serverless API provides an interface for quick experience, allowing you to quickly test the API效果.
Open the Serverless API page, find the Flux.1-dev model under Image Generation and Processing, and click to enter the interface details page.
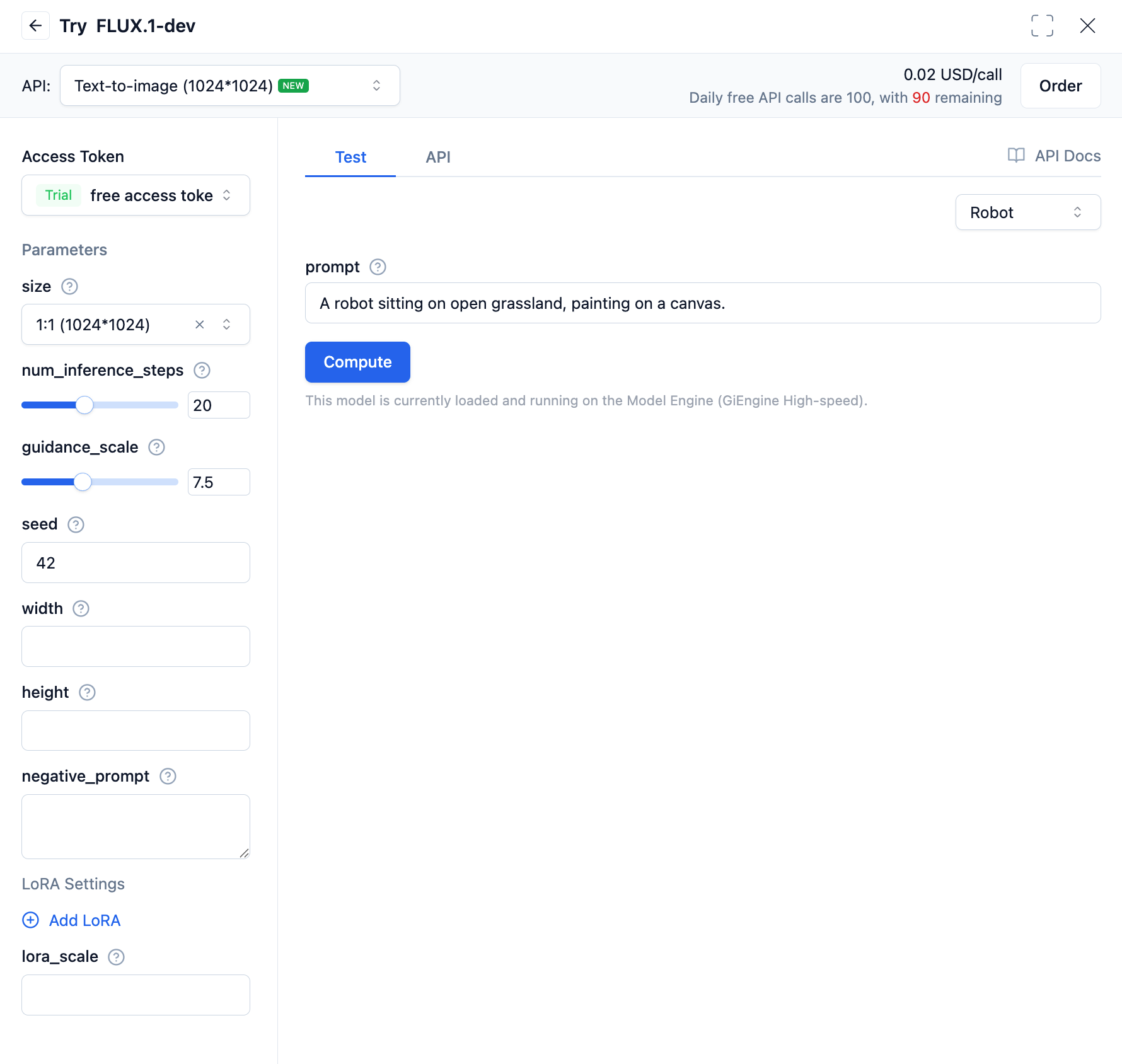
In the text-to-image API, within the LoRA settings: url is the URL of the LoRA model to be loaded; weight is used for weighted fusion between different LoRA model weights; lora_scale is the degree of influence the LoRA model has on the base model.
Calling the Text-to-Image Model
Using OpenAI SDK
The following explains how to use the Flux.1-dev text-to-image LoRA interface through the OpenAI SDK. Here's a Python example:
from openai import OpenAI
import base64
import requests
client = OpenAI(
base_url="https://moark.ai/v1",
api_key="XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX", # Replace with your API Key
)
response = client.images.generate(
prompt="A robot sitting on open grassland, painting on a canvas.",
model="FLUX.1-dev",
size="1024x1024",
extra_body={
"num_inference_steps": 20,
"guidance_scale": 7.5,
"seed": 42,
"lora_weights": [
{
"url": "https://example.com/lora-model.safetensors", # Replace with your LoRA model URL
"weight": 1,
}
],
"lora_scale": 0.5
},
)
for i, image_data in enumerate(response.data):
if image_data.url:
# Download from URL
ext = image_data.url.split('.')[-1].split('?')[0] or "jpg"
filename = f"FLUX.1-dev-output-{i}.{ext}"
response = requests.get(image_data.url, timeout=30)
response.raise_for_status()
with open(filename, "wb") as f:
f.write(response.content)
print(f"Downloaded image to {filename}")
elif image_data.b64_json:
# Decode base64
image_bytes = base64.b64decode(image_data.b64_json)
filename = f"FLUX.1-dev-output-{i}.jpg"
with open(filename, "wb") as f:
f.write(image_bytes)
print(f"Saved image to {filename}")
Using Requests Library
If you prefer not to use the OpenAI SDK, you can directly use the requests library to call the text-to-image model. Here's a Python example:
import requests
import base64
import json
url = "https://moark.ai/v1/images/generations"
headers = {
"Authorization": "Bearer XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX", # Replace with your access token
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"X-Failover-Enabled": "true"
}
data = {
"prompt": "a white siamese cat", # Replace with your text description
"model": "FLUX.1-dev", # Replace with your selected model name
"size": "1024x1024",
"seed": 42,
"response_format": "b64_json",
"num_inference_steps": 25,
"guidance_scale": 7.5,
"lora_weights": [
{
"url": "https://example.com/lora-model.safetensors", # Replace with your LoRA model URL
"weight": 1,
}
],
"lora_scale": 0.5
}
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json=data)
if response.status_code == 200:
for i, image_data in enumerate(response.data):
if image_data.url:
# Download from URL
ext = image_data.url.split('.')[-1].split('?')[0] or "jpg"
filename = f"FLUX.1-dev-output-{i}.{ext}"
response = requests.get(image_data.url, timeout=30)
response.raise_for_status()
with open(filename, "wb") as f:
f.write(response.content)
print(f"Downloaded image to {filename}")
elif image_data.b64_json:
# Decode base64
image_bytes = base64.b64decode(image_data.b64_json)
filename = f"FLUX.1-dev-output-{i}.jpg"
with open(filename, "wb") as f:
f.write(image_bytes)
print(f"Saved image to {filename}")
else:
print(f"Request failed, status code: {response.status_code}")
print(f"Error message: {response.text}")
For other programming languages, you can refer to the sample codes in the API documentation.