Generating Images with ControlNet
Feature Description
ControlNet is a conditional generation-based model that can generate images matching input conditions (such as text, images, etc.). In text-to-image and image editing tasks, ControlNet can be used to generate images that meet specific conditions, such as images of a particular style, specific scenes, etc.
Models Supporting ControlNet
Experience the API Effect
Function Description
The Serverless API provides an interface for quick experience, allowing you to quickly test the API effects.
Open the Serverless API page, find the FLUX.1-dev model under Image Generation and Processing, and click to enter the interface details page.
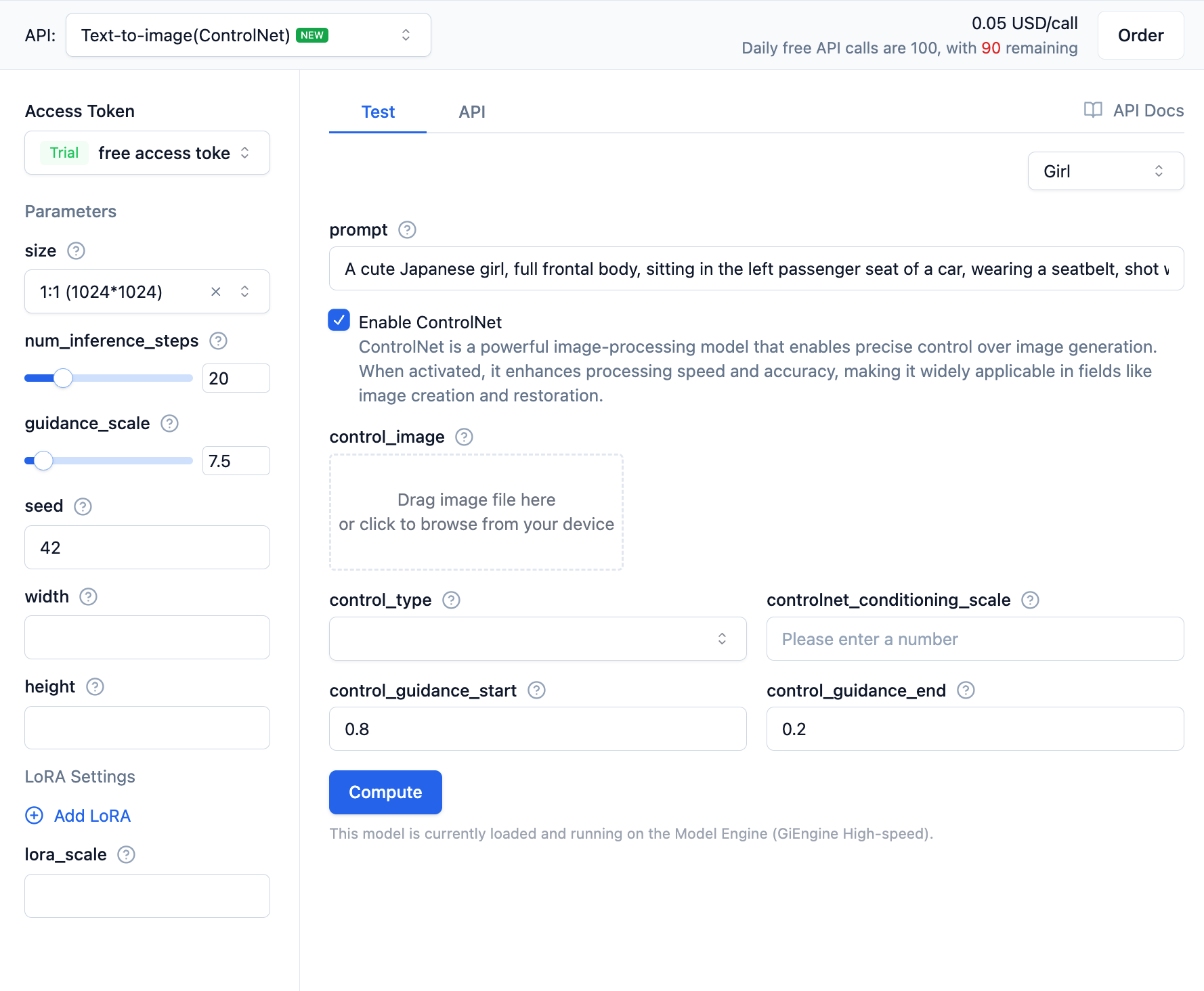
In the text-to-image (ControlNet) interface, after enabling the ControlNet function, you need to set parameters for the ControlNet model.
ControlNet Parameter Explanations:
- control_image: The control image used as a reference for image generation, such as specifying a character's pose or outline to make the generated result more in line with expectations. The control image can be a local image path or an image URL.
- controlnet_type: The type of ControlNet model, with optional values
cannyanddepth.cannyis edge detection, anddepthis depth estimation, used to guide the style or structure of the generated image. - controlnet_conditioning_scale: The degree of influence of the ControlNet model on the base model, ranging from 0 to 1 (floating-point number), with a default value of 0.5. Larger values mean stronger influence from the reference image.
- controlnet_guidance_start: The start time of guidance from the ControlNet model, ranging from 0 to 1 (floating-point number), with a default value of 0.2.
- controlnet_guidance_end: The end time of guidance from the ControlNet model, ranging from 0 to 1 (floating-point number), with a default value of 0.8.
Calling the Text-to-Image Model
Using OpenAI SDK
The following explains how to use the FLUX.1-dev text-to-image ControlNet interface through the OpenAI SDK. Here's a Python example:
from openai import OpenAI
import base64
import requests
client = OpenAI(
base_url="https://ai.gitee.com/v1",
api_key="XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX",
)
response = client.images.generate(
prompt="A robot sitting on open grassland, painting on a canvas.",
model="FLUX.1-dev",
size="1024x1024",
extra_body={
"num_inference_steps": 20,
"guidance_scale": 7.5,
"seed": 42,
"control_image": "https://example.com/image.png", # Replace with your control image URL or base64-encoded image string
"control_type": "canny",
"controlnet_conditioning_scale": 0.5,
"control_guidance_start": 0.8,
"control_guidance_end": 0.2,
},
)
for i, image_data in enumerate(response.data):
if image_data.url:
# Download from URL
ext = image_data.url.split('.')[-1].split('?')[0] or "jpg"
filename = f"FLUX.1-dev-output-{i}.{ext}"
response = requests.get(image_data.url, timeout=30)
response.raise_for_status()
with open(filename, "wb") as f:
f.write(response.content)
print(f"Downloaded image to {filename}")
elif image_data.b64_json:
# Decode base64
image_bytes = base64.b64decode(image_data.b64_json)
filename = f"FLUX.1-dev-output-{i}.jpg"
with open(filename, "wb") as f:
f.write(image_bytes)
print(f"Saved image to {filename}")
Using Requests Library
If you prefer not to use the OpenAI SDK, you can directly use the requests library to call the text-to-image model. Here's a Python example:
import requests
import base64
import json
url = "https://moark.ai/v1/images/generations"
headers = {
"Authorization": "Bearer XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX", # Replace with your access token
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"X-Failover-Enabled": "true"
}
data = {
"prompt": "a white siamese cat", # Replace with your text description
"model": "FLUX.1-dev", # Replace with your selected model name
"size": "1024x1024",
"seed": 42,
"response_format": "b64_json",
"num_inference_steps": 25,
"guidance_scale": 7.5,
"control_image": "https://example.com/image.png", # Replace with your control image URL or base64-encoded image string
"control_type": "canny",
"controlnet_conditioning_scale": 0.5,
"control_guidance_start": 0.8,
"control_guidance_end": 0.2,
}
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json=data)
if response.status_code == 200:
for i, image_data in enumerate(response.data):
if image_data.url:
# Download from URL
ext = image_data.url.split('.')[-1].split('?')[0] or "jpg"
filename = f"FLUX.1-dev-output-{i}.{ext}"
response = requests.get(image_data.url, timeout=30)
response.raise_for_status()
with open(filename, "wb") as f:
f.write(response.content)
print(f"Downloaded image to {filename}")
elif image_data.b64_json:
# Decode base64
image_bytes = base64.b64decode(image_data.b64_json)
filename = f"FLUX.1-dev-output-{i}.jpg"
with open(filename, "wb") as f:
f.write(image_bytes)
print(f"Saved image to {filename}")
else:
print(f"Request failed, status code: {response.status_code}")
print(f"Error message: {response.text}")
Other programming languages can refer to the example code in the API documentation.